MapReduce
MapReduce 是一种编程模型,其思想是让程序员通过编写简单的 Map 和 Reduce 程序就能完成分布式系统的任务,而不需要关注分布式的具体细节。
用户自定义的Map函数接受一个 key/value pair 的输入值,然后产生一个中间 key/value pair 值的集合。MapReduce 库把所有具有相同中间 key 值 I 的中间 value 值集合在一起后传递给 Reduce 函数。
用户自定义的 Reduce 函数接受一个中间 key 的值 I 和相关的一个 value 值的集合。Reduce 函数合并这些 value 值,形成一个较小的 value 值的集合。通常来说,每次 Reduce 函数调用只产生 0 或 1 个输出 value 值。通常我们通过一个迭代器把中间 value 值提供给 Reduce 函数,这样我们就可以处理无法全部放入内存中的大量的 value 值的集合(迭代器可看为一个容器,所以数据放入一个容器中,Reduce 函数就从这个容器中取数据即可)。
例如:计算一个大的文档集合中每个单词出现的次数,Map 和 Reduce 伪代码如下:
| |
MapReduce 框架原理
论文中描述的 MapReduce 框架的具体原理如下:
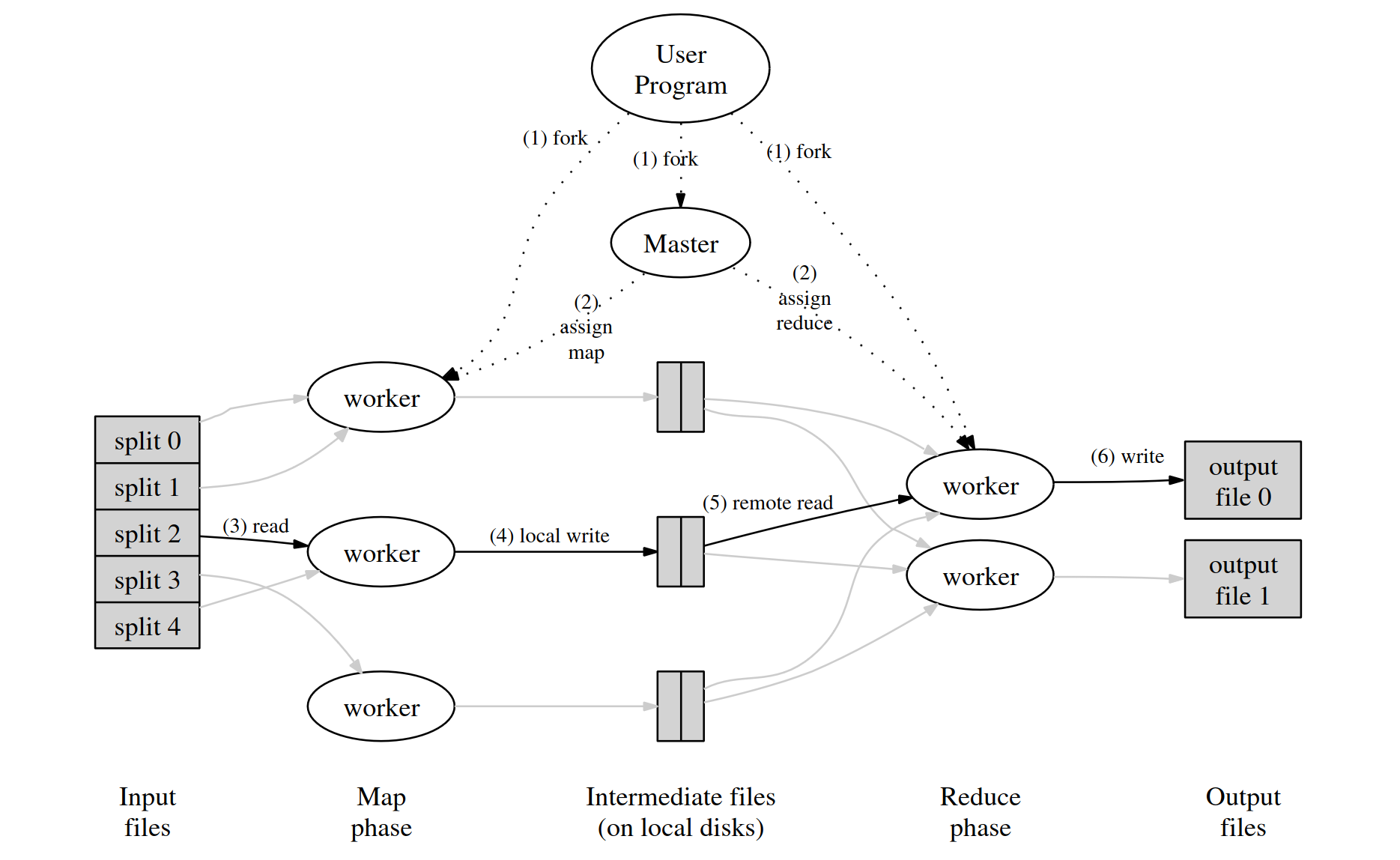
当用户程序调用 MapReduce 时,会发生下面一系列动作:
用户程序首先调用的 MapReduce 库将输入文件分成M个数据片度,每个数据片段的大小一般从 16MB 到 64MB (可以通过可选的参数来控制每个数据片段的大小)。然后用户程序在机群中创建大量的程序副本。
这些程序副本中的有一个特殊的程序 master。副本中其它的程序都是 worker 程序,由 master 分配任务。有 M 个 Map 任务和 R 个 Reduce 任务将被分配,master 将一个 Map 任务或 Reduce 任务分配给一个空闲的 worker。
被分配了 map 任务的 worker 程序读取相关的输入数据片段,从输入的数据片段中解析出 key/value pair,然后把 key/value pair 传递给用户自定义的 Map 函数,由 Map函数生成并输出的中间k ey/value pair,并缓存在内存中。
缓存中的 key/value pair 通过分区函数分成 R 个区域,之后周期性的写入到本地磁盘上。缓存的 key/value pair 在本地磁盘上的存储位置将被回传给 master,由 master 负责把这些存储位置再传送给 Reduce worker。
当 Reduce worker 程序接收到 master 程序发来的数据存储位置信息后,使用 RPC 从 Map worker 所在主机的磁盘上读取这些缓存数据。当 Reduce worker 读取了所有的中间数据后,通过对 key 进行排序后使得具有相同 key 值的数据聚合在一起。由于许多不同的 key 值会映射到相同的 Reduce 任务上,因此必须进行排序。如果中间数据太大无法在内存中完成排序,那么就要在外部进行排序。
Reduce worker 程序遍历排序后的中间数据,对于每一个唯一的中间 key 值,Reduce worker 程序将这个 key 值和它相关的中间 value 值的集合传递给用户自定义的 Reduce函数。Reduce 函数的输出被追加到所属分区的输出文件。
当所有的 Map 和 Reduce 任务都完成之后,master 唤醒用户程序。在这个时候,在用户程序里的对 MapReduce 调用才返回。
First step
在一开始,目标是至少先让代码跑起来。
首先看懂 mrsequential.go 的逻辑,看懂 coordinator 和 worker 的 rpc 交互流程。然后实现 coordinator 分配任务后 worker 直接把任务打印出来。
worker 通过 rpc 调用 coordinator 的 AssignJob 方法,获取任务,然后直接打印出来。
在 rpc.go 中,定义用到的 rpc 相关的结构体:
| |
coordinator.go
| |
worker.go
| |
初步实现(暂不考虑worker出现故障、超时以及一些并发引起的问题,先实现成功调用用户 Map 和 Reduce 方法)
定义结构体用于传递 Map 和 Reduce 需要的参数
| |
暂时考虑对整个 AssignJob 加互斥锁,若发现这样加锁不能满足要求再行改进。
Map worker 将中间文件的文件名传递给 coordinator。
coordinator 将需要 Reduce worker 处理的中间文件的文件名传递给对应的 Reduce worker。
rpc.go
| |
coordinator.go
| |
worker.go
| |
对故障和超时的 worker 的识别和处理,以及一些并发相关问题的解决
对每一个 worker,coordinator 在分配了任务之后等待10秒,若超出10秒 worker 没有完成任务,就把这个 worker 视为 crashed,将任务分配给其他的 worker。
Reduce worker 需要等 Map 全部完成才能开始,在 Map 全部结束之前,利用 channel 阻塞 Reduce worker 的 RPC 调用。
定义两个数组用来显示 map 和 reduce 任务的完成情况。两个 int 类型的变量记录尚未完成的 map 和 reduce 任务的数量,Done 函数通过判断这两个变量来判断 coordinator 任务是否结束。
利用 channel 作为队列,在 coordinator 中定义两个队列,用于存放后面等待分配的 map 和 reduce 任务。分配之后 coordinator 等待10秒,10 秒后任务没有完成就重新把任务放进队列中。
coordinator 在完成对 worker 的调用后新建一个 go routine,等待10秒后判断任务是否已经完成。
worker 在任务成功完成后调用一个 RPC 函数告知 coordinator 任务已完成。
一些注意事项(踩过的坑)
在编写程序时注意函数和变量以大写开头和以小写开头的区别,RPC 模块涉及到的所有函数,传递的变量(包括结构体内部的变量)开头字母都要大写。
使用 go run -race 来检测并发相关的问题。
注意,worker 在执行完一个任务之后应该继续向 coordinator 请求下一个任务,而不是直接返回。
在 worker 中 sleep 一小段时间来避免所有任务被一个 worker 请求而不能通过 parallelism test。
Reduce worker 读取中间文件失败不需要退出,直接尝试读取下一个文件,Map worker 确实可能对于某个 Reduce worker 不产生中间文件。
由于可能会有一些 worker 速度慢,并未 crash 而只是超时,所以会出现一个任务由不同的 worker 先后完成,而向 coordinator 先后多次传递任务完成的信息。所以对于记录剩余未完成的任务的数量的变量,不能收到完成消息后简单减一。
加了锁的函数要注意防止死锁。如 coordinator 的 GetJob 函数中,如果 channel 队列此时为空,会阻塞直到有下一个数进入队列,但若阻塞时互斥锁是 lock 的状态,下一个数进入队列的程序段也加上了锁,将会出现死锁。事实上 GetJob 函数无需加锁。
一个调试了挺久的问题
在快速解决了一些 bug 之后,最后一个问题是 reduce parallelism test 有概率失败,显示“too few parallel reduces”。
我看了一下 test-mr.sh 中的对应内容,也通过随机数给 worker 编号进行了查看,测试失败的原因是只有一个 worker 执行了所有 reduce 进程。
这是为什么呢,我研究了很久,尝试了很多方法都没有找到问题所在。后来我发现每次只有 reduce parallelism test 有可能会出问题,但是 map parallelism test 每次都能正常通过。这让我把问题范围缩小到 map 和 reduce 任务切换处,才终于发现了问题所在。
我的 GetJob 函数是这样写的:
| |
判断 worker 是请求 map 任务还是 reduce 任务是通过剩余未完成的 map 任务的数量来实现的。但考虑当 worker A,B 先后执行最后两个 map 任务 的情况,A 执行完 map 任务后继续请求下一个任务。当 A 加锁取出 c.mapJobsNumLeft 的值时,B 并没有完成任务,于是 A 取出的 c.mapJobsNumLeft 的值为1,会继续请求 map 任务。但此时 map 任务已经全部分配出去,c.mapQueue 是空的,A 将会阻塞在 “reply.MapArgs.WorkerId = <-c.mapQueue” 处,并且只要 B 顺利完成最后一个 map 任务,c.mapQueue 将会一直是空的,A 也就会一直阻塞在此处,不能继续执行后面的 reduce 任务了。
解决方案是不将 worker 阻塞在 channel 处,而是直接判断 channel 是否为空,如果为空就让 worker 等待一段时间再重新请求任务。这样就可以给整个 GetJob 函数加上锁。
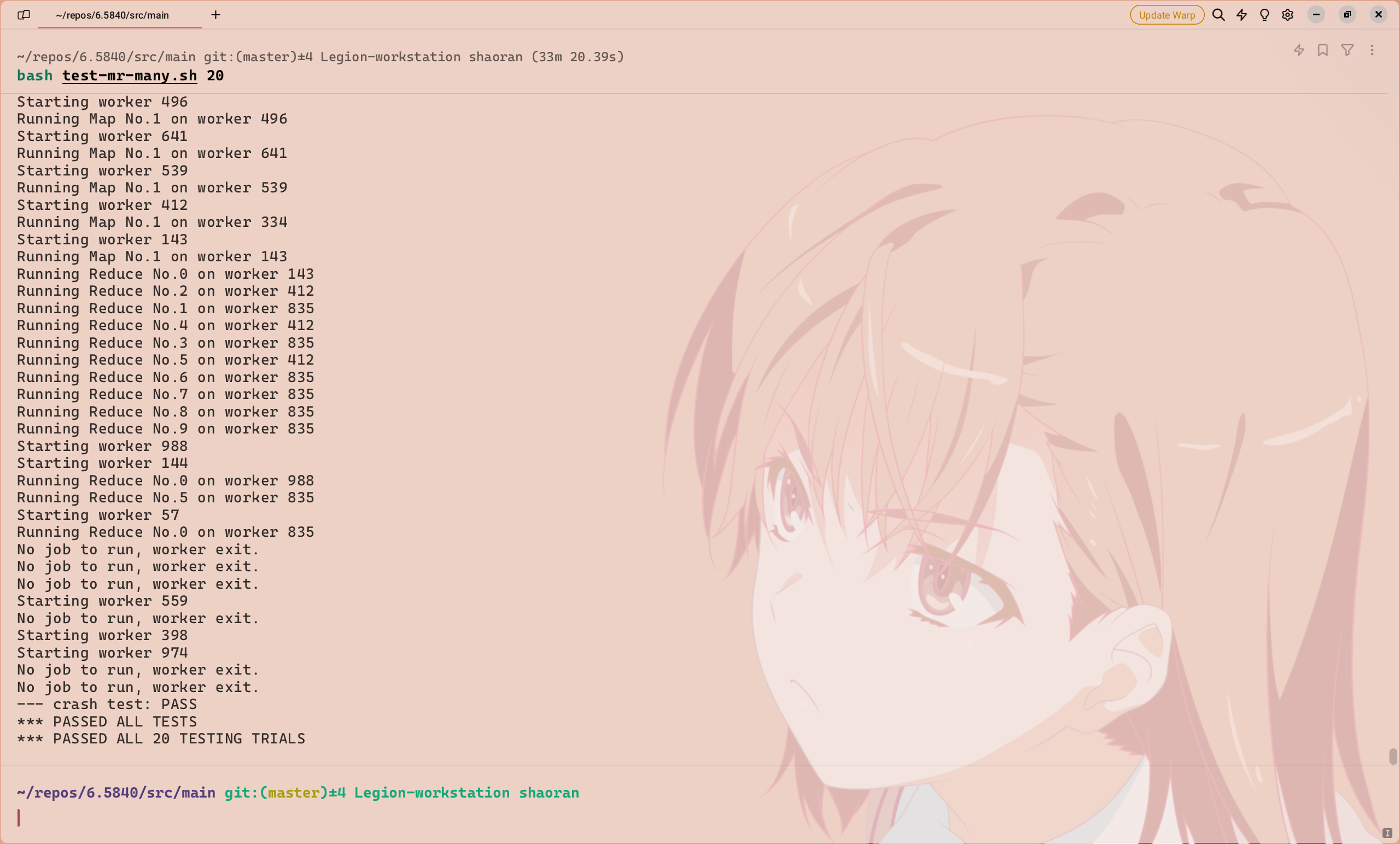
通过全部测试的代码
进行了20次测试,结果如下:
rpc.go
| |
coordinator.go
| |
worker.go
| |